As a board-certified endocrinologist with over 15 years of clinical experience specializing in male hormonal health, I’ve worked with thousands of patients seeking to optimize their testosterone levels naturally. While Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) is an effective medical intervention for clinically diagnosed hypogonadism, many men can significantly improve their testosterone production through evidence-based lifestyle modifications and targeted interventions.
This comprehensive guide examines the scientifically validated approaches to naturally enhance testosterone levels, based on current clinical research and my experience treating patients with hormonal imbalances. We’ll explore the physiological mechanisms behind testosterone production, evidence-based interventions, and practical implementation strategies.
Understanding Testosterone: An Endocrinologist’s Perspective
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone responsible for:
- Muscle mass development and maintenance
- Bone density preservation
- Fat distribution regulation
- Red blood cell production
- Libido and sexual function
- Cognitive function and mood regulation
- Energy levels and overall vitality
Normal testosterone levels typically range from 300-1,000 ng/dL in adult males, with levels gradually declining by approximately 1-2% annually after age 30. However, this decline is not inevitable, and multiple factors within your control can significantly impact testosterone production.
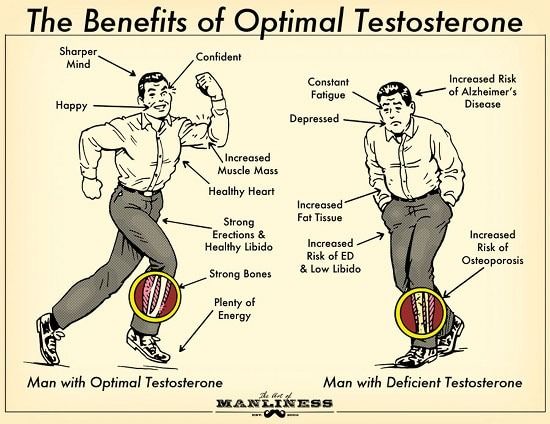
Clinical Signs of Suboptimal Testosterone
Before discussing optimization strategies, it’s important to recognize potential signs of suboptimal testosterone levels:
- Persistent fatigue despite adequate sleep
- Reduced muscle mass despite consistent training
- Increased body fat, particularly in the abdominal region
- Decreased libido and sexual function
- Mood disturbances, including irritability and depressive symptoms
- Cognitive changes, such as reduced concentration and memory
- Reduced motivation and drive
- Sleep disturbances
If you’re experiencing multiple symptoms, I recommend comprehensive hormone testing, including total testosterone, free testosterone, SHBG (Sex Hormone Binding Globulin), estradiol, LH (Luteinizing Hormone), FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone), and prolactin levels. This provides a complete picture of your hormonal status and helps identify specific areas for intervention.
Evidence-Based Strategies for Natural Testosterone Optimization
1. Optimize Body Composition
Body fat percentage has a direct impact on testosterone levels through several mechanisms:
- Aromatase activity: Adipose tissue (particularly visceral fat) contains high levels of aromatase, an enzyme that converts testosterone to estrogen
- Insulin resistance: Excess body fat promotes insulin resistance, which negatively impacts testicular function
- Inflammatory cytokines: Fat tissue secretes inflammatory compounds that can impair hormone production
Clinical evidence: A 2018 study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism demonstrated that men who lost an average of 17% body fat experienced a 15% increase in total testosterone and a 19% increase in free testosterone levels.
Target range: For optimal testosterone production, aim for a body fat percentage between 10-15%. Below 8% can potentially reduce testosterone due to the body perceiving a state of energy deficiency.
Implementation strategy:
- Focus on creating a moderate caloric deficit (300-500 calories below maintenance)
- Emphasize protein intake (1.6-2.2g per kg of body weight)
- Implement a progressive resistance training program
- Include both high-intensity interval training and low-intensity steady-state cardio
2. Strategic Resistance Training
Resistance training is one of the most powerful natural testosterone boosters when properly structured:
- Compound movements: Exercises involving multiple large muscle groups (squats, deadlifts, bench press) stimulate greater hormonal responses
- Volume and intensity: Moderate to high intensity (70-85% of 1RM) with sufficient volume (multiple sets) optimizes testosterone response
- Rest periods: Shorter rest periods (60-90 seconds) for some training sessions can enhance acute hormonal responses
Clinical evidence: A 2021 meta-analysis in Sports Medicine found that resistance training programs emphasizing compound movements with moderate-to-high intensity produced average increases in baseline testosterone levels of 5-10% in previously untrained men after 12 weeks.
Implementation strategy:
- Train 3-5 days weekly
- Focus 70% of training on compound movements
- Cycle between higher intensity (85-90% 1RM) and moderate intensity (70-80% 1RM) phases
- Avoid chronic overtraining, which can elevate cortisol and suppress testosterone
3. Nutrition for Hormonal Health
Dietary choices significantly impact testosterone production through multiple pathways:
- Adequate calories: Chronic severe caloric restriction reduces testosterone production
- Optimal macronutrient distribution: Balanced intake of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats
- Micronutrient sufficiency: Several vitamins and minerals serve as cofactors in testosterone synthesis
Clinical evidence: Research published in the Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology demonstrated that men consuming less than 20% of calories from fat had significantly lower testosterone levels than those consuming 35-40% of calories from fat.
Key dietary recommendations:
- Fat intake: Consume 30-35% of calories from fat, including:
- Monounsaturated fats: Olive oil, avocados, nuts
- Saturated fats: Eggs, grass-fed beef, coconut oil (in moderation)
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Fatty fish, flaxseeds, walnuts
- Carbohydrate optimization:
- Prioritize carbohydrates around training sessions
- Focus on low-glycemic, nutrient-dense sources
- Adjust total carbohydrate intake based on activity level and body composition goals
- Protein requirements:
- Consume 1.6-2.2g of protein per kg of body weight
- Emphasize complete protein sources containing all essential amino acids
- Distribute protein intake throughout the day (20-40g per meal)
- Micronutrient focus:
- Zinc: Oysters, beef, pumpkin seeds, crab (RDA: 11mg daily)
- Magnesium: Dark leafy greens, nuts, avocados (RDA: 400-420mg daily)
- Vitamin D: Fatty fish, egg yolks, sunlight exposure (Target: 2,000-5,000 IU daily)
- Selenium: Brazil nuts, fish, organ meats (RDA: 55mcg daily)
- B vitamins: Whole grains, meat, eggs, dairy
4. Sleep Optimization
Sleep quality and duration directly influence testosterone production through several mechanisms:
- Circadian rhythm regulation: Testosterone production follows a diurnal pattern, with peak production occurring during REM sleep
- Growth hormone secretion: Deep sleep stages promote growth hormone release, which supports testosterone production
- Stress hormone modulation: Proper sleep helps regulate cortisol levels, which inversely relate to testosterone
Clinical evidence: A study in the Journal of the American Medical Association demonstrated that restricting sleep to 5 hours per night for one week reduced testosterone levels by 10-15% in healthy young men.
Implementation strategy:
- Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep nightly
- Maintain consistent sleep-wake cycles
- Create an optimal sleep environment (cool, dark, quiet)
- Limit blue light exposure 1-2 hours before bedtime
- Consider tracking sleep quality with wearable devices
5. Stress Management
Chronic stress elevates cortisol levels, which directly suppress testosterone production:
- HPA axis relationship: The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis regulates both stress and reproductive hormones
- Resource allocation: Under chronic stress, the body prioritizes cortisol production over testosterone
- Sleep disruption: Stress impairs sleep quality, further reducing testosterone production
Clinical evidence: Research published in Hormones and Behavior found that men with chronically elevated cortisol levels had significantly lower free testosterone concentrations compared to age-matched controls with normal cortisol levels.
Effective stress management techniques:
- Mindfulness meditation: 10-20 minutes daily
- Tactical breathing: 4-7-8 breathing method (inhale for 4, hold for 7, exhale for 8)
- Regular physical activity
- Time in nature
- Social connection
- Strategic work-life boundaries
6. Evidence-Based Supplementation
While nutrition should be the foundation, certain supplements have demonstrated efficacy for testosterone optimization:
- Vitamin D3:
- Mechanism: Serves as a steroid hormone precursor
- Evidence: A randomized controlled trial found that men with vitamin D deficiency who supplemented with 3,000 IU daily for 12 months experienced an average 25% increase in testosterone levels
- Dosage: 2,000-5,000 IU daily (based on blood levels, aiming for 40-60 ng/mL)
- Zinc:
- Mechanism: Essential cofactor in testosterone synthesis
- Evidence: Studies show zinc supplementation increases testosterone only in deficient individuals
- Dosage: 25-45mg elemental zinc daily (only if dietary intake is insufficient)
- Magnesium:
- Mechanism: Increases free testosterone by reducing SHBG
- Evidence: Research demonstrates benefits primarily in athletes and physically active individuals
- Dosage: 200-400mg daily (magnesium glycinate or threonate forms)
- Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera):
- Mechanism: Reduces cortisol and supports testicular function
- Evidence: A gold-standard randomized controlled trial found that 600mg daily increased testosterone by 15-18% compared to placebo
- Dosage: 500-600mg standardized extract daily
- Fadogia Agrestis:
- Mechanism: May increase luteinizing hormone and testicular sensitivity
- Evidence: Limited but promising research in animal models; human studies are preliminary
- Dosage: 425-600mg daily (approach with caution due to limited safety data)
Important note: Supplement quality varies significantly. I recommend pharmaceutical-grade supplements tested by third-party organizations for purity and potency.
7. Environmental Factors
Several environmental factors can significantly impact testosterone production:
- Endocrine-disrupting chemicals: Bisphenol A (BPA), phthalates, and certain pesticides can interfere with hormone production
- Thermal exposure: Excessive heat to the testes can impair testosterone synthesis
- Electromagnetic radiation: Some evidence suggests potential impacts from prolonged exposure
Practical recommendations:
- Use glass or stainless steel containers for food storage
- Choose organic produce when possible for the “dirty dozen” foods
- Avoid heating food in plastic containers
- Minimize exposure to thermal sources near the genitals (laptops on laps, hot tubs)
- Consider air and water filtration systems
Clinical Testing and Monitoring
For men serious about optimizing testosterone naturally, I recommend the following testing protocol:
Initial Comprehensive Panel:
- Total testosterone (LC-MS/MS method preferred)
- Free testosterone (calculated or direct)
- SHBG (Sex Hormone Binding Globulin)
- Estradiol (sensitive assay)
- LH (Luteinizing Hormone)
- FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone)
- Prolactin
- Complete metabolic panel
- Lipid profile
- Thyroid function (TSH, Free T3, Free T4)
- Complete blood count
- Vitamin D, magnesium, and zinc levels
Optimal Testing Conditions:
- Morning collection (7-10 AM)
- Fasted state (12 hours)
- Well-hydrated
- Avoiding strenuous exercise for 24 hours prior
- Consistent sleep the preceding night
Monitoring Frequency:
- Baseline testing before implementing changes
- Follow-up testing after 3-4 months of intervention
- Once optimized, testing every 6-12 months
Personalized Implementation Plan
Based on clinical experience, I recommend the following phased approach:
Phase 1 (Weeks 1-4): Foundation Building
- Establish consistent sleep schedule (7-9 hours nightly)
- Implement basic nutrition principles
- Begin resistance training program 3x weekly
- Start daily stress management practice
- Address obvious environmental factors
- Begin basic supplementation (vitamin D, magnesium)
Phase 2 (Weeks 5-12): Progressive Optimization
- Fine-tune nutrition based on body composition changes
- Increase training frequency/intensity if appropriate
- Add advanced supplementation if indicated
- Deepen stress management practice
- Conduct first follow-up testing (week 12)
Phase 3 (Months 4-6): Individualization
- Make evidence-based adjustments based on testing results
- Address any identified deficiencies or imbalances
- Consider more targeted interventions based on specific hormonal patterns
- Implement advanced training techniques if progress plateaus
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How long does it take to see results from natural testosterone optimization?
Most men notice subjective improvements in energy, mood, and libido within 4-6 weeks of implementing comprehensive lifestyle changes. Measurable increases in testosterone levels typically require 8-12 weeks of consistent implementation. Maximum benefits are usually achieved within 6-12 months.
Can natural approaches match the results of TRT?
For men with clinical hypogonadism (testosterone below 300 ng/dL) due to testicular or pituitary dysfunction, natural approaches are unlikely to match TRT results. However, for men with borderline or low-normal levels (300-500 ng/dL), comprehensive natural intervention can often increase levels by 100-200 ng/dL, which is clinically significant.
Does age affect the potential for natural testosterone optimization?
Age influences potential outcomes but doesn’t eliminate the possibility of improvement. Men in their 30s-40s typically see the largest percentage increases (sometimes 30-50% above baseline), while men in their 50s-60s may experience more modest improvements (15-25% above baseline). Even men in their 70s can achieve measurable increases with comprehensive lifestyle modification.
How do I know if I need TRT despite natural interventions?
Consider TRT consultation if:
- You’ve implemented comprehensive lifestyle changes for 6+ months with minimal results
- Your total testosterone remains below 350 ng/dL despite interventions
- You experience significant symptoms impacting quality of life
- You have identifiable medical causes of hypogonadism (pituitary disorders, testicular injury, genetic conditions)
Can natural testosterone optimization benefit men already on TRT?
Absolutely. The strategies outlined in this guide can help:
- Potentially reduce the required TRT dosage
- Optimize free testosterone levels
- Improve testosterone:estrogen ratio
- Enhance overall health markers
- Reduce potential side effects of TRT
How does weight loss affect testosterone?
Weight loss improves testosterone levels primarily by:
- Reducing aromatase activity (less conversion of testosterone to estrogen)
- Improving insulin sensitivity
- Decreasing inflammatory markers
- Enhancing sleep quality
However, extremely rapid weight loss or maintaining very low body fat percentages can potentially lower testosterone. The sweet spot appears to be a body fat range of 10-15% achieved through gradual, sustainable methods.
Do herbal testosterone boosters work?
Most over-the-counter “testosterone boosters” contain ingredients with minimal scientific support. The supplements with the strongest evidence include:
- Ashwagandha (clinically proven)
- Tongkat Ali (moderate evidence)
- Fadogia Agrestis (preliminary evidence)
- Shilajit (moderate evidence for free testosterone)
Always choose single-ingredient supplements from reputable manufacturers and monitor your response with proper testing.
Conclusion
As an endocrinologist specializing in male hormonal health, I’ve witnessed remarkable improvements in testosterone levels and overall wellbeing in patients who implement these evidence-based strategies. While natural approaches require more effort than simply starting TRT, they address the root causes of declining testosterone and offer comprehensive health benefits beyond hormonal optimization.
Remember that testosterone optimization is a marathon, not a sprint. Consistent implementation of these strategies over months produces far better results than short-term extreme approaches. Work with knowledgeable healthcare providers who can help you monitor your progress objectively and make evidence-based adjustments to your protocol.